Water Testing -
Bacteria/Algae Control -
Inline Digital Sensor
3:56
Water Testing -
Bacteria/Algae Control -
MIC - Microbially
Influenced Corrosion
9:31
Water Testing -
Bacteria/Algae Control -
MIC in Chiller
1:11
Water Testing -
Bacteria/Algae Control -
MIC in Fire Sprinklers
1:42
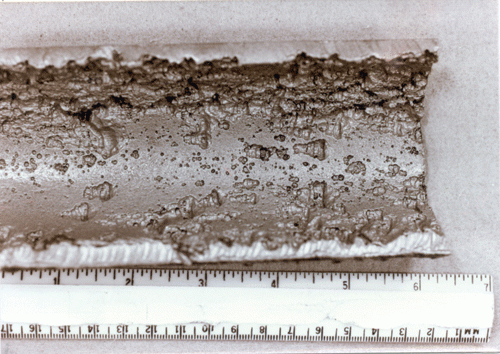
Caustic Attack
Caustic gouging


Caustic attack on boilers is due to extremely high pH (>12.9 ). It can take two forms: caustic gouging or caustic cracking, also called caustic embrittlement.
Caustic cracking usually occurs where stress has been placed on the steel, such as tube's rolled ends or the bent section of a water tube.


Caustic Cracking

Video:
Water Testing -
Caustic Embrittlement -
Caustic Cracking
5:42
Carryover Control
Videos:
Carryover, also known as priming, is when boiler water droplets travel with steam into the steam lines and in generally caused by the following:
1) High TDS. Surface tension increases and bubbles stabilize. Foaming occurs. Bubble level rises beyond boiler control design. Some bubbles escape with the steam.
2) High Demand Swing. Excessively large swings in demand causes pressure in boiler to drop. To compensate, bubble size increases and water level rises. Swell occurs as bubble layer raises above boiler control design. Some bubbles may then escape with steam.

Mechanical Controls
Automatic

Inline Conductivity Probe
Motorized valve
Controller
Surface Blowdown
Manual Surface Blowdown Valve

Separators and Scrubbers

Risers
Downcomers
Risers
Water Testing -
Carryover Control -
TDS Control
1:46
Water Testing -
Carryover Control -
Swell
When pressure drops and temperature stays the same, the volume has to increase.
Therefore, the bubbles swell.
2:18
P x V = T
Combined Gas Law
Fe Corrosion Detection
.jpg)
Dissolved Carbon Dioxide (CO ) gas in water is not corrosive . However, it breaks down and forms carbonic acid (H CO ), which is corrosive for mild steel up to pH 8.3 . Condensate pH levels should be kept above this limit if using neutralizing amines. This corrosion can be detected in the condensate via iron titration kits. If this dissolved iron makes it back to the boiler, iron scale may form on boiler tubes. Iron scale acts as an insulator, affecting heat transfer ability, reducing efficiency.
2
2
3

Videos:
Water Testing -
Fe Corrosion Detection -
Corrosion Coupon
3:52
Can be easily added to cooling water lines and steam lines.
1:36
Water Testing -
Fe Corrosion Detection -
Corrosion Microcell
1:36
Water Testing -
Fe Corrosion Detection -
Corrosion Coupon Analysis
3:20
Water Testing -
Fe Corrosion Detection -
DI/RO Makeup Water
DI = Deionized RO = Reverse Osmosis
By removing carbonates from makeup water, Carbon Dioxide is greatly reduced in condensate.
Freeze Control


2:23
Water Testing -
Freeze Control -
Why Do Pipes Burst?
10:03
Water Testing -
Freeze Control -
Tips to keep pipes from
freezing
1:47
Water Testing -
Freeze Control -
Heat Trace
Metal Passivation
The creation of a relatively inert protective layer (usually an oxide) on metal surfaces.
Stainless Steel
Zn as a Passivator
10:27
Water Testing -
Metal Passivation -
Passivation and White Rust
Oxygen Corrosion
Water + Iron + Heat = Instant rust
IF there is oxygen in the water.
Oxygen needs to be removed from water before it gets to the boiler:
1) By raising the temperature
a) Steam Boilers: Deaerator
b) Hydronic Boilers: Makeup Water Mixing Tanks (allows water to raise to room temp before using)
2) Adding an oxygen scavenger
a) High Pressure Boiler: DEHA
b) All others: Sulfite

(Including hydronic boilers if unit uses significant amount of makeup water or system contains non-oxygen barrier tubing)
Videos
Water Testing -
Carryover Control -
Steam Drum
1:26
Water Testing -
Oxygen Corrosion -
Gas Solubility vs Temperature
3:14
Water Testing -
Oxygen Corrosion -
Gas Solubility vs Pressure
0:36
Water Testing -
Oxygen Corrosion -
Ultrasonic Degassing
1:46
Not presently used in boiler systems.
See Also:
Water Testing -
Oxygen Corrosion -
Ultrasonic Degas of Beverage
0:36
Scale Prevention
Temporary Hardness = Carbonate Hardness
Generally, an increase in water temperature causes an increase in the solubility of most salts.
HOWEVER, this is just the opposite for Ca(CHO3)2 and Mg(CHO3)2, which become less soluble as temperature increases. They 'fall out of' (or precipitate out of) solution and become scale deposits on the hottest part of the boiler: the tubes.
This is referred to as Temporary Hardness because boiling the water removes it.
Permanent Hardness
Permanent hardness cannot be "boiled out". It must be chemically treated and filtered or mechanically removed via Ion Exchangers. It consist of CaCl2, MgCl2 (Chlorides), CaSO4 and MgSO4 (Sulfates).
Videos
Water Testing -
Scale Prevention -
Temporary vs Permanent
Hardness
4:21
Water Testing -
Scale Prevention -
Soft & Hard Water vs Soap
3:30
Water Testing -
Scale Prevention -
Making Hard Water Soft
4:18
1:41
Water Testing -
Metal Passivation -
Pickling and Passivation
Carbonic Acid
.jpg)
Dissolved Carbon Dioxide (CO ) gas in water is not corrosive . However, it breaks down and forms carbonic acid (H CO ), which is corrosive for mild steel up to pH 8.3 . Condensate pH levels should be kept above this limit if using neutralizing amines. Amines boil, condense and travel along with water neutralizing carbonic acid in condensate. To avoid wasting chemical during blowdowns, amines are typically injected directly into steam lines instead of feedwater.
2
2
3

Most common neutralizing amines: